This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Vyhledávání
Numerical simulations
Numerical simulations enable the virtual testing of a future product; and the optimization of its properties or the elimination of its failures.
Software tools
Preprocessing
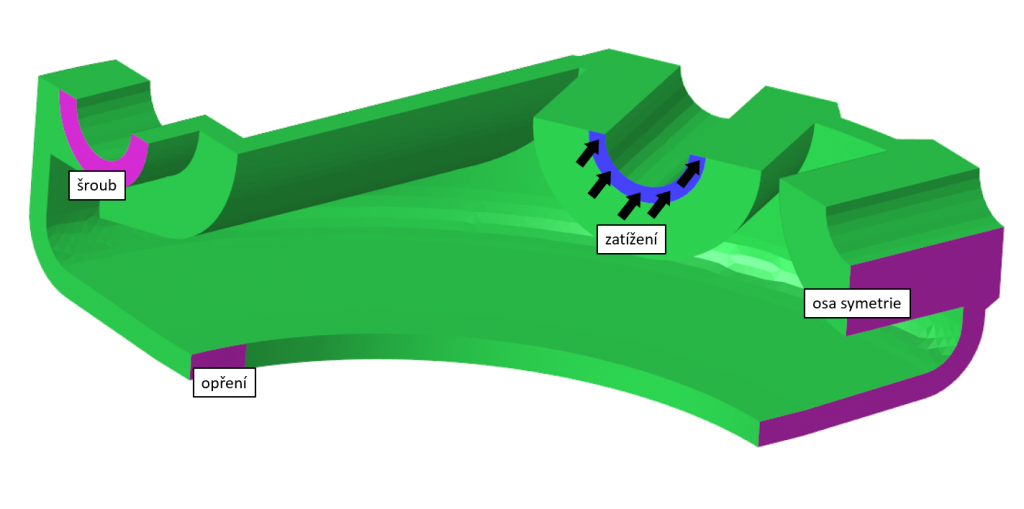
Preprocessing is the preparation of a model for computational analysis (FEM). Before the actual analysis, it is necessary to insert constraints and loads and define material properties or other computational model parameters – calculation type, contact parameters, convergence criteria, output physical quantities of the analysis etc. More >>
Available in the NCC for MATCA:
HyperMesh, Inspire, SimLab
Meshing
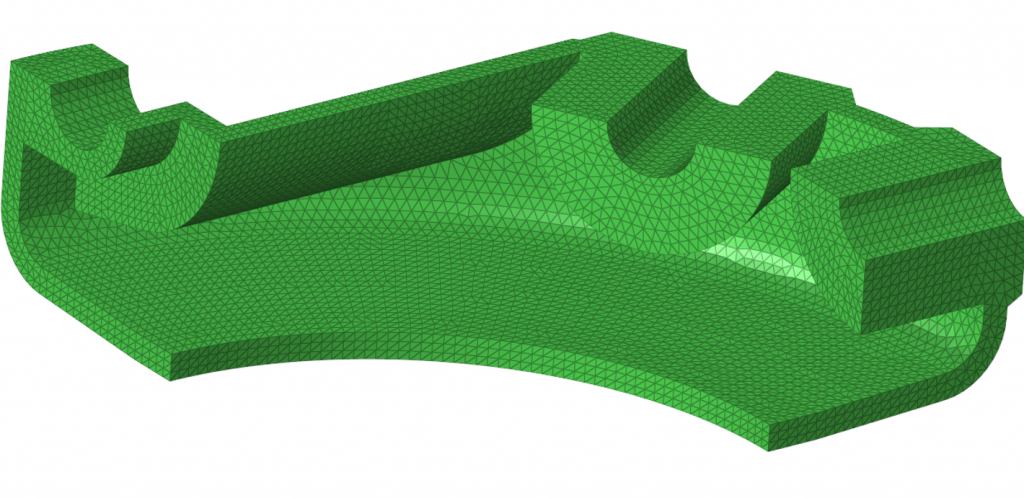
A software used for generating a suitable mesh that is applied to the geometry of given mechanical part (created by a designer in CAD) for the finite element method (FEM). This mesh can be created in 1D, 2D or 3D, depending on the part and the calculation type. More >>
Available in the NCC for MATCA:
HyperMesh, Inspire, SimLab
Solvers
A solver is the actual solver of an FEM task. It can either provide only a linear problem solution or, linear or non-linear solution. The solved problems can include tasks such as material strength (deformation or tensile force from a load), modal (determining of the actual shapes and frequencies) or thermal (heat transfer). The solver can also handle numerical solutions for acoustic and vibrational problems, fatigue strength, as well as electromagnetism, or liquid flow. More >>
Available in the NCC for MATCA:
Optistruct, Radioss, Inspire, SimLab
Postprocessing
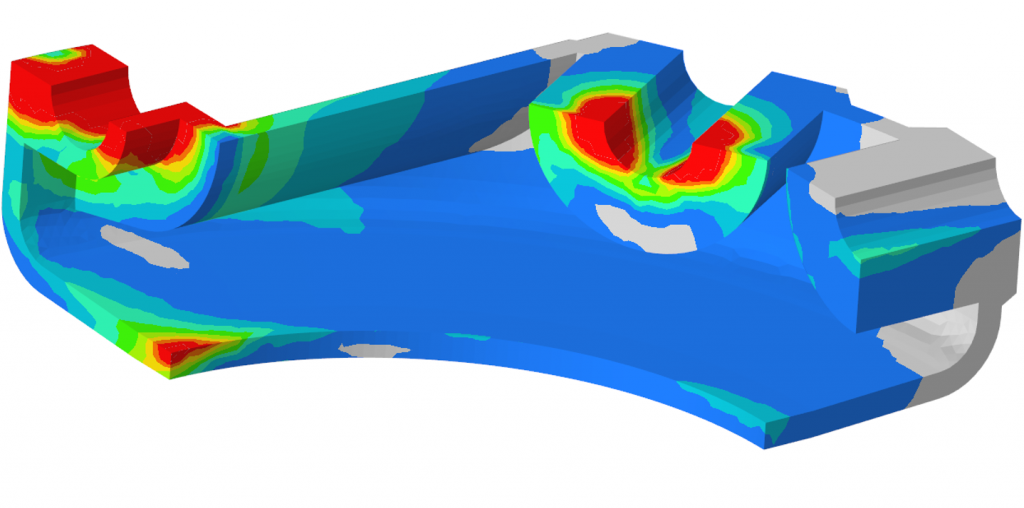
As a follow up to the outputs from the FEM solver, the postprocessing enables the assessment of analysis results. The results can be shown as maps (such as tensile map), graphs, tables, or other visual representations, enabling the processing of the analysis results. More >>
Available in the NCC for MATCA:
HyperView, HyperGraph
Optimization
Optimization means the determination of an “ideal” shape, thickness, distribution, and materials in terms of primarily the part’s weight or stiffness. The calculation of the optimization process requires that the model is prepared in a way similar to that of the analysis; that optimization parameters are set up and FEM solvers used for own solution of a single optimization cycle. The optimization module must also ensure the management of the optimization run in the iteration cycle: change in model parameters – FEM analysis – the evaluation of the destination function, of boundary conditions. More >>
Available in the NCC for MATCA:
Inspire, SimLab

 The NCK for MATCA is supported by the
The NCK for MATCA is supported by the